Failure and Metallurgical Analyses
Sheppard T. Powell Associates, LLC (STPA) has performed over 6,000 metallurgical jobs for our clients primarily in the power and pulp & paper industries. Typically, metallurgical jobs involve one to eight tube samples, although some of these jobs have involved 30 or more tube samples. While most of these metallurgical jobs were based largely on determining deposit weight and performing composition analyses for boiler and HRSG tubes, many have involved metallurgical, remaining life, and other evaluations of these and related components. For tubes, pipes and fittings in condensers, cooling water systems, heating water systems, and fire protection systems, STPA has performed dimensional assessments, remaining life assessments, and failure analyses. Some microstructural or failure examinations also require the additional services of outside laboratories, which are billed at cost (e.g., metal composition or DNA analyses).
In recent years, a large portion of our time has been spent on failure analyses of numerous tubes and pipes with a lesser amount of time spent on other types of other power plant equipment. Our current technical team has expertise with all types of failure mechanisms experienced at power plants. STPA also has been requested to perform or assist plants with root cause analyses and provide assistance for boiler tube and HRSG tube failure prevention programs. STPA provided the first draft and led the development of an industry guide on tube sample collection, shipment and analyses.

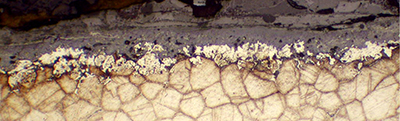
- Bead Blast Method of Deposit Weight (ASTM D3483, Method C / NACE TM-0199-99)
- Characterization of Corrosion Products, Scale Or Water-Formed Deposits
- Composition Analyses of Deposits
- Deposit Thickness (Micrometer and Metallographic Deposit Thickness Measurements)
- Dimensional Assessments
- Elemental Mapping
- Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDXS)
- Failure Analysis or Evaluation of Damage Mechanisms
- Ammonia Grooving
- Cavitation
- Corrosion-Assisted Thermal Fatigue
- Corrosion Fatigue
- Cracking
- Creep
- Dealloying Corrosion (Dezincification, Denickelification)
- Decarburization
- Dew Point Corrosion
- Dissimilar Metal Welds
- Enoblement
- Erosion
- Fatigue
- Fireside Corrosion
- Flow-Accelerated Corrosion (FAC)
- Formicary Corrosion Damage
- Fretting Corrosion Failures
- Galvanic Corrosion
- General Corrosion
- Gouging (Acid Phosphate Corrosion/Phosphate Gouging, Caustic Gouging)
- Graphitic Corrosion
- Graphitization
- High Temperature Oxidation
- Hydrogen Damage
- Liquid Ash Corrosion
- Liquid Metal Embrittlement
- Overheating
- Pitting (Acid, Oxygen)
- Spheroidization
- Stress-Assisted Corrosion
- Stress-Corrosion Cracking
- Sulfidation
- Thermal Fatigue Failures
- Underdeposit Corrosion
- Hardness Testing
- Identification Of Casting And Manufacturing Defects
- Mechanical Method of Deposit Weight (ASTM D3483, Method A)
- Metallography
- Metallurgical Analyses or Investigations
- Mounting Specimens
- Pit Depth and Wall Thickness Measurements
- Remaining Life Assessments
- Research and Evaluate Problem, – serve as Expert Witness for Depositions and Testimony
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
- Stereo Microscopy
